Comprehensive Guide to Calculating and Analysing Profit and Loss in Restaurants
Stay informed with industry news, tips, and practical guides for hospitality professionals.
Running a successful restaurant involves much more than just serving delicious food and drinks. A key factor that determines whether a restaurant thrives or struggles is the ability to manage its finances effectively. Understanding how to calculate and analyse profit and loss is essential for restaurant owners, managers, and financial teams. Proper financial analysis helps in making informed decisions, controlling costs, and ultimately ensuring profitability.
In this blog, we will explore comprehensive methods to calculate and analyse profit and loss in restaurants, focusing on the key elements that contribute to financial health and growth.
Understanding Key Financial Terminology
Before diving into the calculation methods, it’s crucial to understand some of the key terms used in restaurant finance. These terms will help you navigate profit and loss statements (P&L) and understand how various factors impact your restaurant's bottom line:
- Revenue (Sales): The total amount of money your restaurant earns from food and beverage sales, including tips and other income sources.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs of producing the food and beverages you sell, including ingredients, beverages, and packaging.
- Gross Profit: Revenue minus COGS. This represents the profit made after covering the costs directly related to food and beverage production.
- Operating Expenses: The costs associated with running your restaurant, including rent, utilities, wages, marketing, and other overheads.
- Net Profit: The final profit after all expenses (including operating expenses, taxes, and interest) have been deducted from the gross profit.
Calculating Gross Profit Margin
One of the most important metrics in understanding restaurant profitability is the gross profit margin. This metric indicates how much profit your restaurant makes after deducting the cost of ingredients from the revenue. A healthy gross profit margin is essential for sustaining the business, as it shows how efficiently the restaurant is turning its sales into actual profit.
Formula:
Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue x 100
Example:
If your restaurant generates £50,000 in sales for the month, and the cost of goods sold is £20,000, the calculation would be:
(£50,000 - £20,000) / £50,000 x 100 = 60%
A 60% gross profit margin means that for every £1 in sales, your restaurant makes 60p in profit after covering the cost of ingredients.
Why it matters:
Monitoring your gross profit margin helps you assess whether your pricing strategy, portion sizes, and ingredient costs are aligned with your revenue goals. If the margin is too low, it may indicate issues with cost control or pricing strategies.
Tracking Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the indirect costs that go into running your restaurant. These expenses include rent, utilities, staff wages, marketing, and other overhead costs. Tracking these expenses closely is crucial to understanding your restaurant’s overall profitability.
Categories of Operating Expenses:
- Labour Costs: This includes wages, salaries, benefits, and tips for employees. Labour costs can be one of the biggest expenses for restaurants, so managing them effectively is key to maintaining profitability.
- Rent and Utilities: Costs related to your restaurant’s location and the services it uses, such as electricity, water, and internet.
- Marketing and Advertising: Expenses for promoting your restaurant, including social media, print ads, promotions, and loyalty programmes.
- Other Overheads: This includes equipment maintenance, insurance, supplies, and any other ongoing costs.
Why it matters:
By monitoring operating expenses, you can identify areas where you might be overspending and take action to cut unnecessary costs. Keeping a close eye on labour costs, for example, ensures that your restaurant operates efficiently without overstaffing.
Calculating Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin is one of the most comprehensive indicators of your restaurant’s overall profitability. It measures how much of your revenue remains as profit after all expenses are deducted, including operating expenses, interest, and taxes.
Formula:
Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Revenue x 100
Example:
If your restaurant generates £50,000 in revenue and your total expenses (including COGS, operating expenses, taxes, and interest) total £45,000, your net profit is £5,000.
The net profit margin would be:
£5,000 / £50,000 x 100 = 10%
Why it matters:
A higher net profit margin indicates that your restaurant is efficiently converting sales into actual profit after all expenses. A low or negative net profit margin could signal problems that need addressing, such as high operating costs or low sales.
Identifying Key Profit Drivers and Areas for Improvement
Once you have calculated your profit and loss, it's important to analyse the results in detail. Here are some key areas to consider when looking for ways to increase profitability:
- Menu Optimisation: Evaluate the profitability of each menu item. Use your P&L statement to identify dishes with high food costs or low margins and consider adjusting prices, portion sizes, or ingredient choices.
- Waste Reduction: Monitor food waste closely. If your restaurant has high food waste, you may be losing money unnecessarily. Implementing inventory management systems can help reduce waste and lower COGS.
- Labour Efficiency: Use your P&L statement to track your labour costs as a percentage of revenue. If labour costs are too high, look at ways to improve scheduling, reduce overtime, and streamline operations.
- Sales and Marketing: Ensure that your marketing strategies are driving traffic and sales effectively. Monitor promotions, special events, and loyalty programmes to assess their return on investment.
Why it matters:
Understanding the drivers behind your profit and loss statement allows you to take proactive steps to enhance profitability. Whether it’s adjusting your menu or improving efficiency, informed decisions based on your P&L analysis can make a significant difference.
Using Financial Software for Better Analysis
In today’s fast-paced restaurant industry, manual calculations can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Using restaurant-specific financial software can streamline the process of tracking and analysing profit and loss.
Benefits of Financial Software:
- Automated Reporting: Financial software can automatically generate profit and loss statements, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Real-Time Data: Many software programs offer real-time financial insights, so you can monitor performance and make quick decisions.
- Inventory and Labour Integration: Some software tools integrate with inventory management and scheduling systems, making it easier to track COGS and labour costs in real-time.
- Forecasting Tools: Advanced software can help you predict future profits and plan accordingly by analysing past trends and external factors like seasonality.
Popular Restaurant Financial Software:
- Xero: A cloud-based accounting software that helps with invoicing, payroll, and generating profit and loss reports.
- QuickBooks: Offers comprehensive financial tools and integrates well with other restaurant management software.
- MarketMan: Focuses on inventory and procurement management, helping control food costs and monitor COGS.
Why it matters:
Investing in financial software enables more accurate and efficient tracking of profit and loss, providing restaurant owners with the tools to make data-driven decisions and stay on top of their finances.
Conclusion
Calculating and analysing profit and loss is an essential practice for running a profitable restaurant. By understanding key financial terms, calculating gross and net profit margins, and tracking operating expenses, restaurant owners and managers can gain a clearer picture of their business's financial health. Implementing smart financial practices and using modern software tools can help streamline the process, improve efficiency, and identify opportunities for growth. Regularly reviewing your profit and loss statements and making adjustments based on the data will ultimately lead to a more successful, sustainable restaurant business.
Ready to simplify hospitality ops?
We’ve got you.
Speak with an Opsyte expert to see how we help:
- Save hours on staff scheduling and rota planning
- Automate invoice processing and financial insights
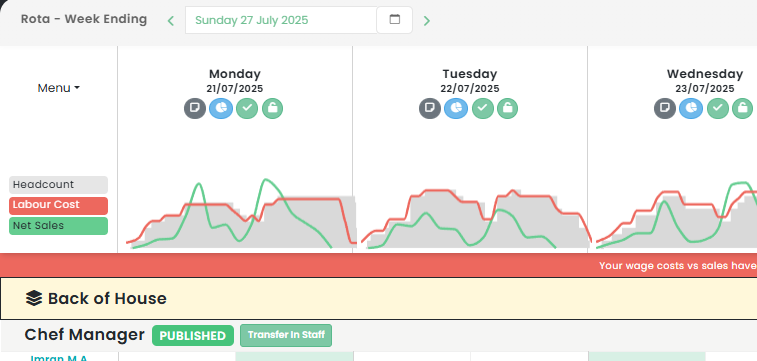
- Track live labour costs vs sales in real-time
- Get fast answers and support from real humans
- Automate your P&Ls
“Opsyte transformed our entire back office. Game changer.”
Read articles from our hospitality experts
-
Maximising Nightlife Entertainment: Innovative Pub Event Ideas and Marketing Strategies for the Hospitality Industry
Revitalise Your Hospitality Business with Creative Pub Event IdeasIn the dynamic and competitive hospitality industry, especially within the sphere of UK pubs, crafting engaging and unique event ideas is crucial…...
-
Boosting Restaurant Productivity: Discover the Best Scheduling Apps and Management Software for the Hospitality Industry
Best Scheduling App for Restaurants: Improving Efficiency in the UK Hospitality IndustryAs we venture deeper into the digital age, the need for efficient and reliable restaurant management software has become…...
-
Maximising Workforce Efficiency: The Ultimate Guide to Rota Software and Shift Planning in Hospitality Management
Revolutionising the Hospitality Industry with Rota SoftwareThe hospitality industry in the UK is a bustling, dynamic environment. To maintain a smooth operation, efficient scheduling solutions, like Rota Software, have become…...
-
Leveraging Hospitality App Development: The Future of Hotel and Restaurant Management in the Mobile Era
Hospitality App Development: A Game Changer for UK Hospitality IndustryIn the dynamic digital landscape, the hospitality industry is continually evolving, and the demand for innovative technology solutions, particularly mobile apps,…...
-
Boosting Employee Satisfaction: The Impact of Implementing a Living Wage in the Hospitality Industry
The Impact of the Living Wage on the UK Hospitality IndustryThe UK hospitality industry has been at the forefront of numerous discussions on wage standards, compensation, and labor rights. One…...
-
Boost Your Bar Sales: Creative Drink Promotions and Marketing Ideas for the Hospitality Industry
Revitalising Hospitality: Innovative Drink Promotions Ideas for SuccessThe UK hospitality sector, with its vibrant nightlife, lively pubs, and eclectic restaurants, thrives on creativity and innovation. One key to success in…...
